This poster was originally presented at ISPOR Europe, November 6-9, 2022, in Vienna, Austria.
Authors: Andrew Shim, A. Singhania, Dave Iwanyckyj, F. Otalora, B. Morrison, SW Wade
Affiliations: Turning Point Therapeutics, San Diego, CA, USA; Amplity, Bucks, UK; Wade Outcomes Research and Consulting, Salt Lake City, UT, USA
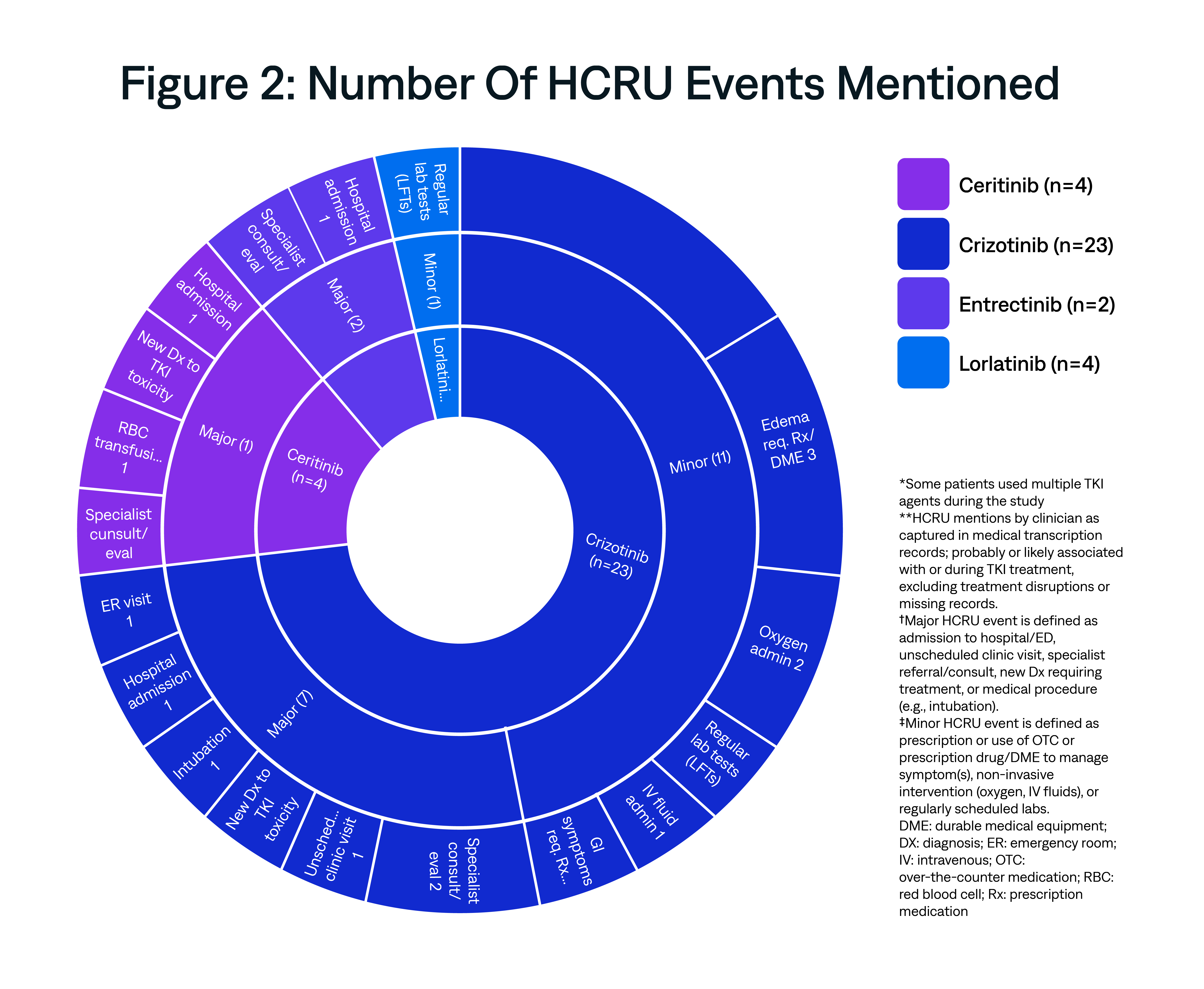
This exploratory analysis examined the unexpected healthcare resource utilization (HCRU) of ROS1+ non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients using data from physician narratives of real-world patient encounters in the U.S. routine care setting.
AnswerY gets to the “why” behind prescriber rationale. See other NSCLC-related research.